Environmental Assessment
Volume B-4.3
Mine
Fish and Aquatic Resources
Ambatovy Project
252
January 2006
•
physical removal or disturbance of instream habitat (stream channels or
ponds);
•
changes in water flow downstream; and
•
changes in surface water quality.
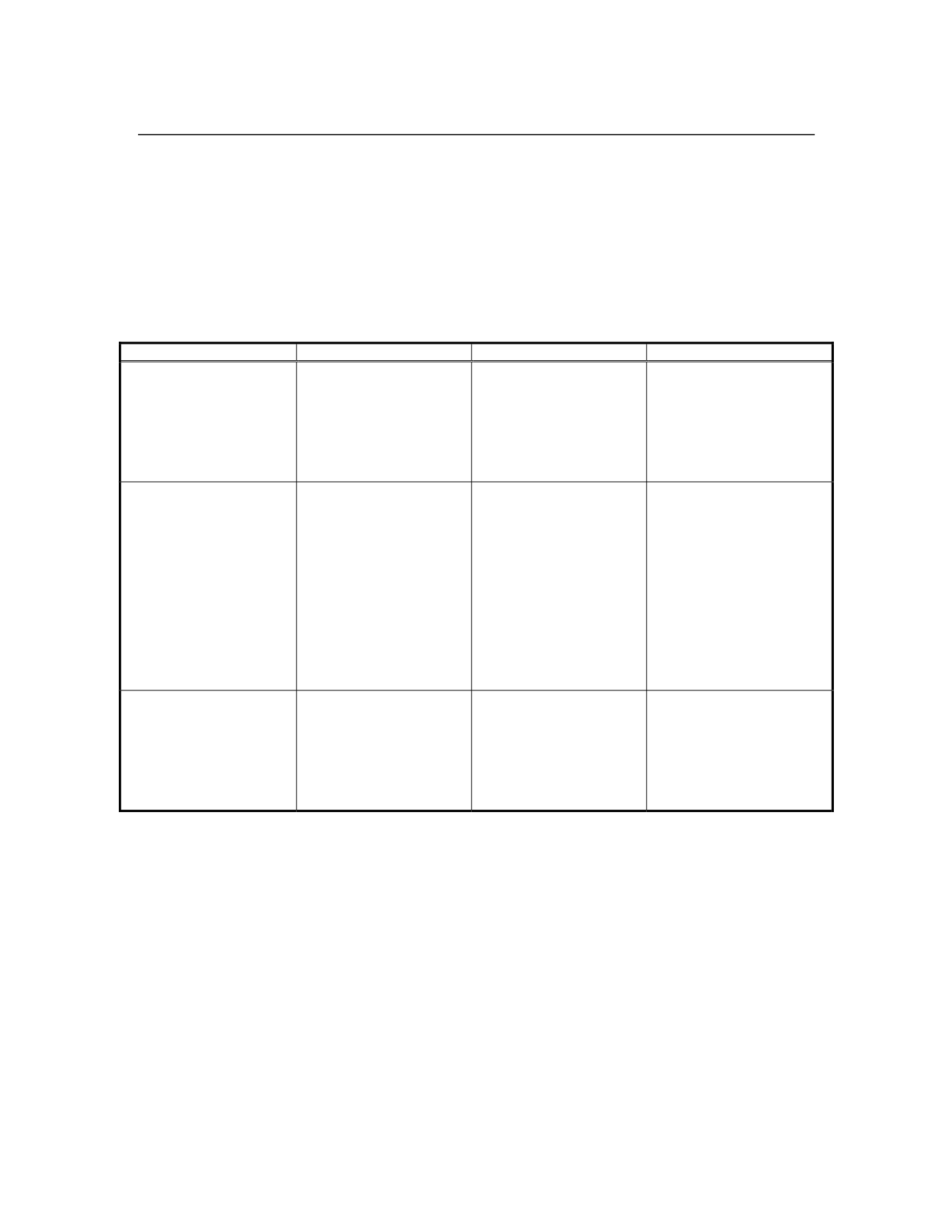
Table 4.3-4 Ecosystem Components, Parameters and Criteria for Fish and
Aquatic Resources
Question
Ecosystem Component
Measurable Parameter
Evaluation Criteria
change in the quality and
availability of aquatic habitat
headwater streams,
ephemeral ponds, endemic
fish, benthic macro-
invertebrates
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
stream order and
exclusion length
pond number and area
water flow and prediction
of fish habitat based on
estimated area
reclamation habitat type
net loss of fish habitat
water quality and
suspended sediment
guidelines
qualitative assessment of
long-term changes to
aquatic biota community
structure
change in abundance of
aquatic biota, survival of
endemic species and
aquatic community structure
endemic and native fish,
benthic macro-invertebrates
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
fish/ invertebrate
community structure and
diversity
results of physical habitat
and aquatic health
assessments
plant operations, water
intake, tailings discharge
potential for transfer of
fish and biota ; harvest
pressure
subjective evaluation of
sustainability of the
resource; professional
judgment
conservation status (IUCN
2004 and published
checklists)
intake screening design
considerations
water quality guidelines for
the protection of aquatic life
(CCME 1999)
watercourse crossings
design considerations
change in fish health, quality
and use
artisanal fisheries
-
-
-
-
-
-
surface water quality and
prediction
metal concentrations in
baseline fish tissue
predicted fish abundance
World Bank Environment,
Health and Safety
Guidelines for Mining and
Milling – Open Pit
suggested values from the
literature
subjective evaluation and
professional judgment
Riparian Vegetation Removal
Clearing of riparian vegetation, associated forest canopy and disturbance of the
riparian zone results in an indirect loss of aquatic habitat through alteration and
loss of terrestrial food sources for aquatic biota, and changes to physical
limnology (e.g., water temperatures) and water quality (e.g., sedimentation)
affecting the ability of biota to survive or complete critical life history functions.
A majority of riparian clearing will occur during mine construction and
expansion and is directly linked to removal of the local area stream channels and
ponds (below). Riparian disturbance will also occur during construction of the
water intake (Mangoro River) and the water pipeline watercourse crossings.


